Genome Engineering
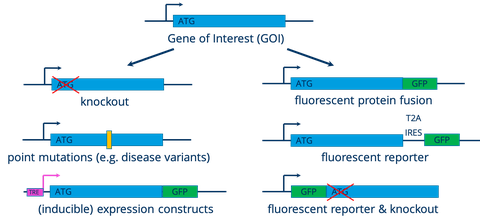
Pluripotent stem cells can be engineered using CRISPR/Cas9 technology or other molecular genetic techniques to generate various sublines with specific features:
- CRISPR/Cas9 assisted targeting of the human safe harbor locus AAVS1 to stably integrate (inducible) expression constructs
- CRISPR/Cas9 assisted targeting of endogenous genes to generate fluorescent reporters, protein fusions etc.
- Flp or Cre mediated excision of selection cassettes after targeting
- PiggyBAC transposition for stable integration of reporter or expression constructs
- gene knockouts by CRISPR/Cas9
- repair or mutation of single or few nucleotides (e.g. disease associated point mutations) to generate isogenic pairs of control and disease iPSC lines by:
- Homology directed repair (HDR) using Cas9-NLS protein, in vitro transcribed sgRNA and ssDNA oligonucleotides as template.
- Base editing using sgRNAs and Adenine or Cytosine base editor (ABE or CBE) mRNA in collaboration with the Buchholz laboratory.
- NEW: Prime editing using pegRNA and prime editor (PE) mRNA in collaboration with the Buchholz laboratory.
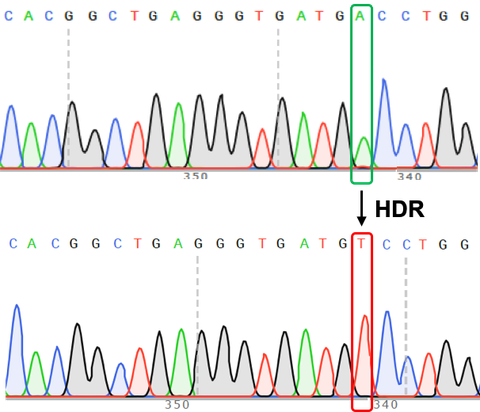
Chromatograms of the original gene locus and the same locus after homogy directed repair (HDR) to correct one base pair.
If possible, 2 engineered clones per parental line are generated for each project. Importantly, the efficiency of Genome Engineering highly depends on the genomic context and no guarantee that the chosen strategy works or the cell line functions as anticipated can be given.

Wildtype FUS protein tagged with FusionRed and mutant FUS with eGFP in human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) for the Sterneckert lab (CRTD).